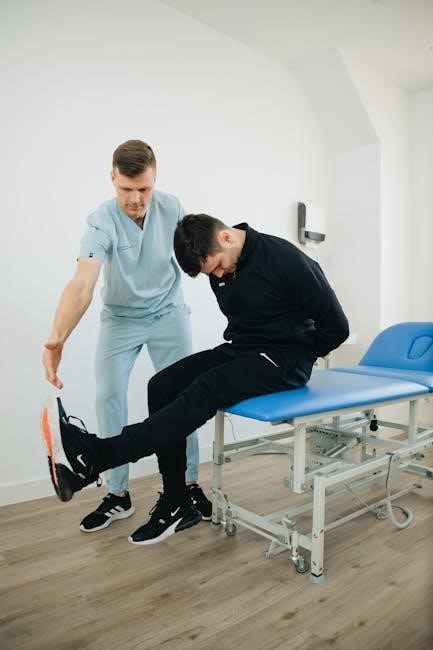
Manual stretching involves using external force, often from a therapist or trainer, to lengthen muscles. This hands-on approach aims to increase flexibility and range of motion beyond what one can achieve independently.
Definition of Manual Stretching
Manual stretching is a technique where a trained professional, like a physical therapist or certified trainer, applies external force to stretch a client’s muscles. Unlike self-stretching, this method allows for a deeper and more controlled stretch, targeting specific muscle groups and addressing restrictions that an individual might not be able to reach on their own. The practitioner uses their hands to guide the limb or body part through a range of motion, applying gentle pressure to lengthen the targeted muscles and improve flexibility. This approach often incorporates specific techniques to enhance muscle relaxation and reduce resistance, ultimately leading to improved range of motion and reduced pain.
Benefits of Manual Stretching
Manual stretching offers several benefits beyond traditional self-stretching. It allows for a more targeted approach, addressing specific muscle imbalances and restrictions with the guidance of a trained professional. This can lead to improved flexibility and range of motion, as the practitioner can apply precise pressure and techniques to lengthen muscles effectively. Furthermore, manual stretching can help reduce pain and muscle tension by releasing trigger points and promoting relaxation. It can also enhance posture and body awareness, contributing to better movement patterns and reduced risk of injury. Integrating manual stretching into a routine can optimize physical performance and overall well-being.
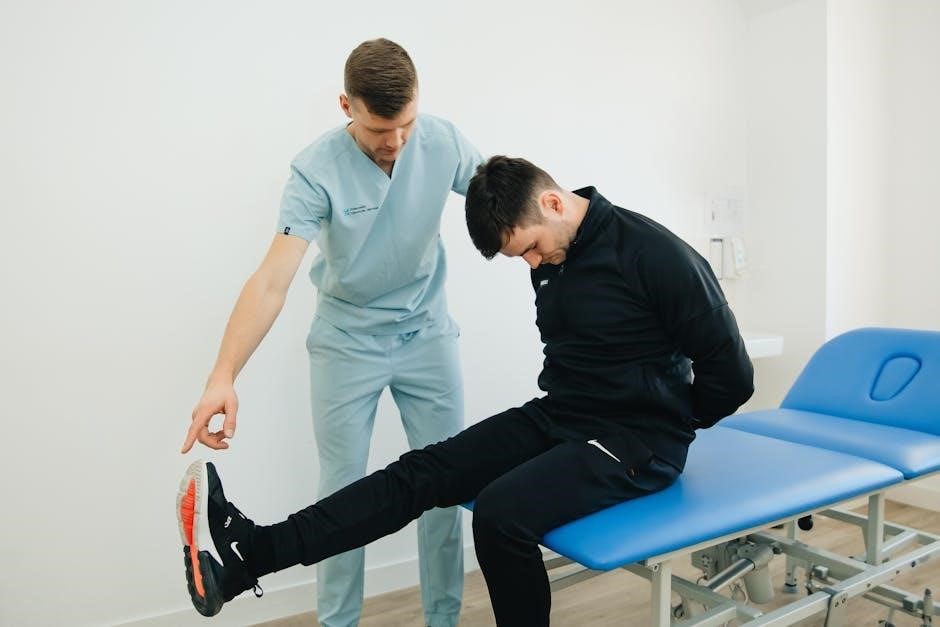
Types of Manual Stretching Techniques
Static stretching, a common technique, involves holding a muscle in a lengthened position for a sustained period. This promotes relaxation and increased flexibility over time, enhancing overall range of motion.
Static Stretching
Static stretching is a technique where a muscle is gently extended and held in a lengthened position for a specific duration, typically ranging from 15 to 60 seconds. This sustained stretch allows the muscle fibers to relax and elongate, leading to increased flexibility and range of motion. Static stretching is commonly performed as part of a cool-down routine to reduce muscle soreness and improve overall flexibility. It’s important to avoid bouncing or jerking movements during a static stretch, as this can increase the risk of injury. Proper breathing and relaxation are key to maximizing the benefits of static stretching and promoting muscle recovery. Moreover, consistent static stretching can contribute to better posture and reduced muscle imbalances.
Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) Stretching
Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) stretching is an advanced technique that combines assisted stretching with muscle contractions to improve flexibility and range of motion. This method often involves a partner who provides resistance during muscle contractions and assistance during stretches. A common PNF technique involves contracting the target muscle against resistance, followed by a period of relaxation and assisted stretching. This process helps to override the body’s natural reflexes that limit flexibility, allowing for deeper and more effective stretches. PNF stretching is known to be highly effective for increasing flexibility, but it requires proper instruction and caution to avoid injury. It may also be more effective for immediate gains.
Dynamic Stretching
Dynamic stretching involves controlled, movement-based stretches that prepare the body for activity. Unlike static stretching, which involves holding a stretch for an extended period, dynamic stretches are performed through a full range of motion. Examples include arm circles, leg swings, and torso twists. These movements increase blood flow to the muscles, improve joint mobility, and enhance neuromuscular coordination. Dynamic stretching is an effective way to warm up muscles and reduce the risk of injury before exercise. Dynamic stretches should be performed smoothly and gradually, avoiding bouncing or jerky movements. This type of stretching is an important component of a comprehensive fitness routine.
Manual stretching enhances flexibility and joint range of motion. It reduces muscle tightness, allowing for greater movement and improved physical performance and minimizes the risk of muscle related injuries.
Improved Flexibility and Range of Motion
Manual stretching significantly enhances flexibility by lengthening muscles beyond their typical capacity. This increased muscle length translates to a greater range of motion in the joints, enabling smoother and more efficient movement. Improved flexibility reduces stiffness, making everyday activities easier and more comfortable. Enhanced range of motion contributes to better athletic performance, allowing for more powerful and controlled movements. Regular manual stretching can also correct muscle imbalances, leading to improved posture and reduced risk of injury. By addressing muscle tightness, manual stretching promotes overall physical well-being and a greater sense of ease in movement. This method can be particularly beneficial for individuals with limited flexibility due to sedentary lifestyles or specific physical conditions.
Pain Reduction and Management
Manual stretching is effective for pain reduction by releasing muscle tension and trigger points. Techniques like Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) can immediately reduce pain associated with trigger points. Addressing muscle imbalances can alleviate chronic musculoskeletal pain; Stretching increases tolerance to stretch, leading to long-term pain management. Improved flexibility and range of motion reduce strain on joints, diminishing pain. Stretching promotes circulation, aiding in tissue repair and pain relief. Reduced muscle tightness decreases pressure on nerves, alleviating nerve pain. The release of endorphins during stretching contributes to a natural pain-relieving effect. Regular stretching can prevent pain recurrence by maintaining muscle flexibility. This approach offers a non-pharmacological method for managing and reducing various types of pain, enhancing overall comfort and quality of life.

Benefits of Manual Stretching
Injury Prevention
Manual stretching plays a crucial role in injury prevention by enhancing muscle flexibility and joint range of motion. Increased flexibility reduces the risk of muscle strains, pulls, and joint injuries during physical activities. Stretching improves the muscle-tendon unit’s ability to withstand stress, preventing injuries. Regular stretching maintains healthy joint range of motion, lowering the chances of joint and muscle strain. Improved muscle elasticity and temperature prepare the body for exercise, reducing injury risk. Stretching addresses muscle imbalances, preventing compensatory movements that can lead to injuries. By promoting better posture and mobility, manual stretching reduces the risk of injuries related to poor body mechanics. Integrating stretching into warm-up and cool-down routines further minimizes injury potential. Overall, manual stretching contributes significantly to injury prevention by optimizing muscle and joint health.

Risks and Precautions
While beneficial, manual stretching carries risks like muscle strain, joint pain, and nerve damage if performed incorrectly. Proper instruction and guidance from a qualified professional are crucial to minimize these risks.
Potential for Muscle Strain and Injury
Manual stretching, while effective, presents a risk of muscle strain and injury if not performed correctly. Excessive force or improper technique can overstretch the muscle fibers, leading to micro-tears or even more significant strains. Individuals with pre-existing musculoskeletal conditions are particularly vulnerable and should exercise extra caution. It’s essential to listen to your body and communicate any discomfort to the practitioner. Ignoring pain signals can exacerbate existing issues and lead to chronic problems. Always prioritize proper form and gradual progression over aggressive stretching to minimize the potential for muscle strain and injury during manual stretching sessions.
Importance of Proper Instruction and Guidance
Proper instruction and guidance are paramount in manual stretching to ensure safety and maximize benefits. A qualified therapist or trainer can assess individual needs, identify limitations, and tailor stretching techniques accordingly. They provide real-time feedback, correcting posture and preventing overextension. This personalized approach reduces the risk of injury and enhances the effectiveness of each stretch. Guidance also involves educating individuals about proper breathing, muscle engagement, and post-stretch recovery. Understanding these principles empowers individuals to perform self-assisted stretches safely and maintain flexibility gains. Seeking expert guidance is crucial for a safe and effective manual stretching experience, especially for those with pre-existing conditions or limited flexibility.

Manual Stretching and Injury Prevention
Manual stretching plays a key role in injury prevention by improving flexibility and range of motion. This can help muscles withstand greater stress, reducing the risk of strains and tears.
Role in Reducing Muscle Injuries
Manual stretching contributes significantly to reducing muscle injuries by enhancing muscle elasticity and preparing them for physical activity. Tight muscles are more prone to strains and tears, but manual stretching helps lengthen these muscles, improving their ability to absorb force and withstand stress. By increasing flexibility, manual stretching also allows for a greater range of motion, reducing the likelihood of exceeding the muscle’s capacity during movement. Regular manual stretching can address muscle imbalances and improve overall muscle health, further minimizing the risk of injury during exercise or daily activities. This proactive approach supports long-term physical well-being.
Impact on Joint Health
Manual stretching significantly impacts joint health by improving range of motion and reducing stiffness. When muscles surrounding a joint are tight, they can restrict movement and contribute to joint pain and dysfunction. Manual stretching helps lengthen these muscles, allowing the joint to move more freely and comfortably. This increased range of motion can reduce stress on the joint surfaces, minimizing the risk of wear and tear. Furthermore, manual stretching promotes better joint lubrication by encouraging synovial fluid circulation. This fluid nourishes the joint cartilage and helps reduce friction during movement. Regular manual stretching contributes to long-term joint health, preventing stiffness and maintaining optimal function.
Integrating Manual Stretching into an Exercise Routine
Incorporating manual stretching into your routine enhances flexibility, reduces injury risk, and improves overall performance. Strategic integration maximizes benefits for both pre- and post-workout recovery and mobility.
Pre- and Post-Workout Stretching
Integrating manual stretching before and after workouts can significantly improve flexibility, reduce injury risk, and enhance recovery. Pre-workout manual stretching prepares muscles by increasing blood flow and range of motion, optimizing performance and reducing the likelihood of strains or pulls. Dynamic stretches, facilitated by a partner or therapist, are particularly effective in this phase.
Post-workout, manual stretching aids in muscle recovery by reducing tension and promoting relaxation. Static or PNF stretches can help alleviate soreness and improve joint range of motion. Consistency in incorporating these stretches optimizes flexibility gains and supports long-term muscle health, ensuring a well-rounded fitness routine.
Frequency and Duration Recommendations
For optimal benefits, manual stretching should be performed consistently, ideally 2-3 times per week, targeting major muscle groups. Each stretching session should last between 15 to 30 minutes, allowing sufficient time to address multiple areas. Hold each stretch for 20-30 seconds, focusing on deep breathing and relaxation to enhance muscle lengthening.
Individuals with specific needs, such as athletes or those recovering from injuries, may benefit from more frequent sessions. Consulting with a physical therapist or certified trainer is crucial to tailor the frequency and duration based on individual flexibility levels, fitness goals, and any underlying conditions. Proper guidance ensures safe and effective stretching practices.